Africa, a continent of astounding diversity and rich cultural heritage, is also blessed with a vast array of resources that have the potential to drive economic growth and development.
From the sweeping deserts to lush rainforests, each African country boasts a unique blend of resources that shape its economic trajectory.
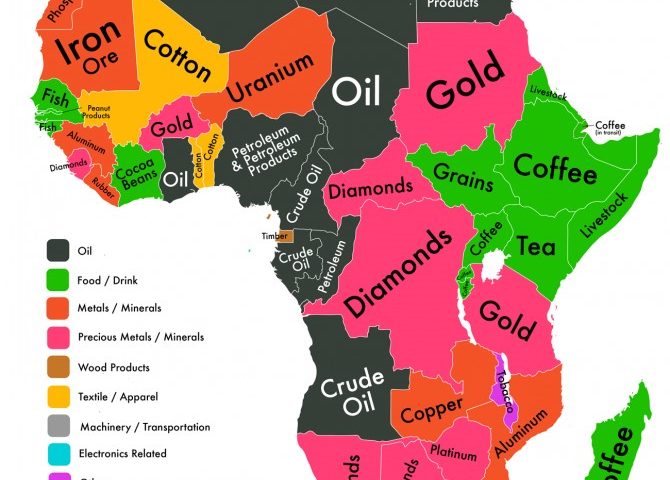
Here is a list of all African countries along with some information on the resources that have the potential to contribute to their economic development:
1. Algeria: Natural gas and oil reserves can provide significant revenue.
2. Angola: Abundant oil and diamond resources are central to its economy.
3. Benin: Agriculture, including cotton, palm oil, and cocoa, contributes to its economy.
4. Botswana: Diamonds are a major source of revenue, along with mining and tourism.
5. Burkina Faso: Gold mining and agriculture, particularly cotton, are important sectors.
6. Burundi: Agricultural products like coffee and tea are crucial for its economy.
7. Cabo Verde: Tourism, services, and fishing contribute to its economy.
8. Cameroon: Oil, timber, and agricultural products like cocoa and coffee are key.
9. Central African Republic: Mining (diamonds, gold, uranium) and agriculture are vital.
10. Chad: Oil and agriculture, including livestock and cotton, are important sectors.
11. Comoros: Agriculture and fishing are central to its economy.
12. Congo (Brazzaville): Oil, timber, and mineral resources play a significant role.
13. Congo (Kinshasa): Rich in mineral resources like cobalt, copper, and diamonds.
14. Cote d’Ivoire: Cocoa, coffee, and oil contribute to its economy.
15. Djibouti: Strategic location for trade, port services, and limited mineral resources.
16. Egypt: Tourism, Suez Canal revenue, and natural gas are economic drivers.
17. Equatorial Guinea: Oil and gas resources are the backbone of its economy.
18. Eritrea: Agriculture, mining, and potentially significant mineral deposits.
19. Eswatini: Agriculture, particularly sugarcane and forestry products.
20. Ethiopia: Agriculture, including coffee, and growing manufacturing sector.
21. Gabon: Rich in oil, manganese, and other mineral resources.
22. Gambia: Agriculture, tourism, and fishing are key sectors.
23. Ghana: Gold, cocoa, and oil are significant contributors to its economy.
24. Guinea: Bauxite and iron ore are valuable resources.
25. Guinea-Bissau: Agriculture and fishing contribute to its economy.
26. Kenya: Agriculture, tea, coffee, tourism, and geothermal energy.
27. Lesotho: Water resources and textile manufacturing are important.
28. Liberia: Iron ore, rubber, and agriculture play vital roles.
29. Libya: Oil reserves are central to its economy.
30. Madagascar: Rich in minerals (nickel, cobalt), agriculture, and tourism.
31. Malawi: Agriculture, particularly tobacco and tea, is vital.
32. Mali: Gold mining and agriculture are key sectors.
33. Mauritania: Abundant mineral resources, particularly iron ore and gold.
34. Mauritius: Tourism, textiles, and services are economic drivers.
35. Morocco: Phosphates, agriculture, and growing industrial sector.
36. Mozambique: Natural gas, coal, and agriculture are important.
37. Namibia: Diamonds, uranium, and fisheries are central to its economy.
38. Niger: Uranium and agriculture, including livestock, are significant.
39. Nigeria: Oil, agriculture, and a growing tech industry are economic pillars.
40. Rwanda: Coffee, tea, tourism, and ICT are important sectors.
41. Sao Tome and Principe: Fisheries, agriculture, and potential oil reserves.
42. Senegal: Fishing, phosphates, and agriculture contribute to its economy.
43. Seychelles: Tourism and fishing are economic drivers.
44. Sierra Leone: Diamonds, agriculture, and fisheries are significant.
45. Somalia: Agriculture, fishing, and potentially oil resources.
46. South Africa: Diverse mineral resources, agriculture, and manufacturing.
47. South Sudan: Oil reserves are central to its economy.
48. Sudan: Oil, agriculture, and minerals play important roles.
49. Tanzania: Agriculture, mining, and tourism are key sectors.
50. Togo: Phosphates, agriculture, and mining contribute to its economy.
51. Tunisia: Tourism, textiles, and agriculture are significant.
52. Uganda: Agriculture, including coffee, and potential oil reserves.
53. Zambia: Copper mining, agriculture, and tourism.
54. Zimbabwe: Mineral resources like platinum and agriculture.
The wealth potential of these resources can vary based on factors like market demand, technology, infrastructure, governance, and global economic conditions. Effective management, sustainable practices, and inclusive policies are essential to ensure that these resources contribute to the long-term prosperity of these African countries.