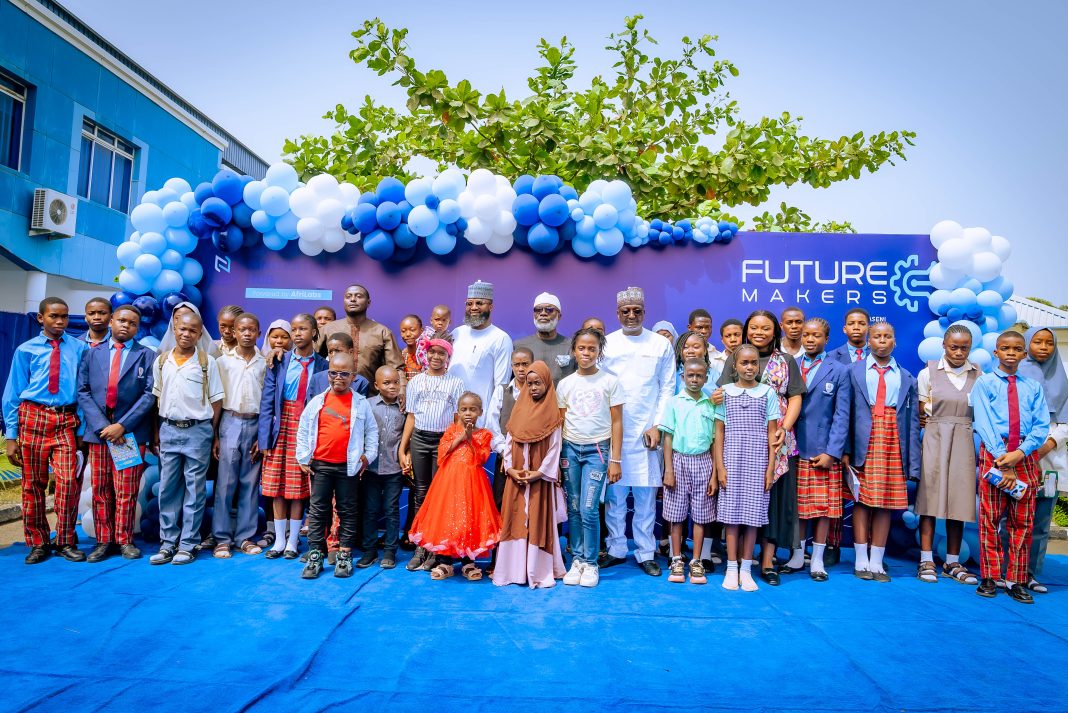
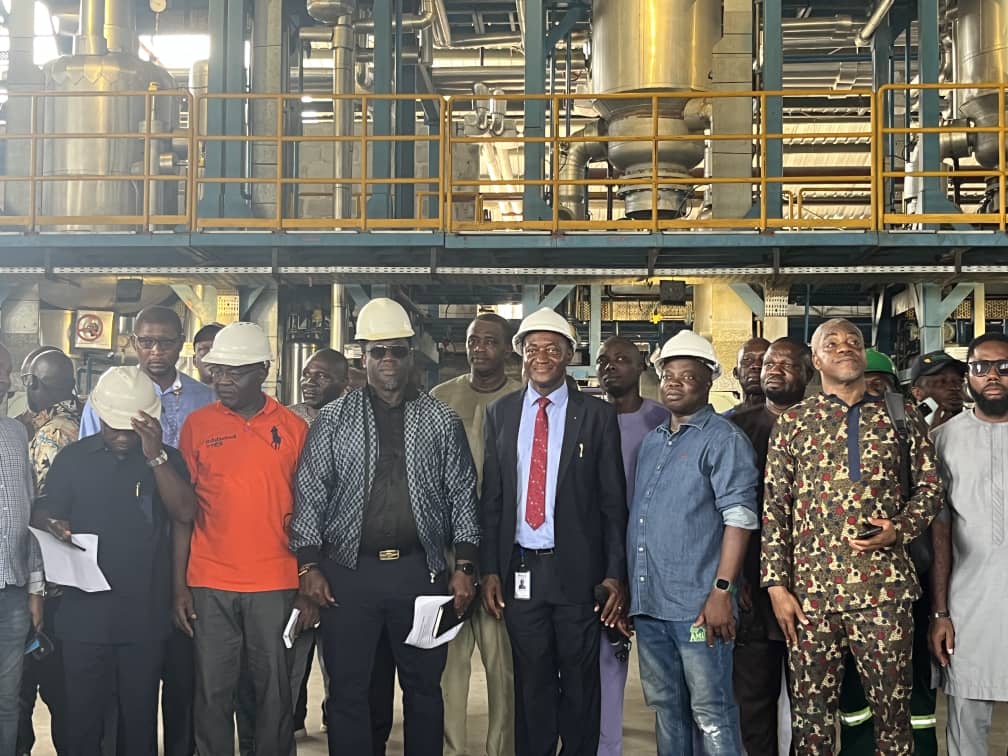
Nigeria’s Giant Strides in the Implementation of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction
Since the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in 2015, Nigeria has demonstrated strong political will and institutional commitment to domesticate and accelerate the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). At the heart of this effort is the Office of the Senior Special Assistant to the President on SDGs (OSSAP-SDGs), which has championed strategic policies, frameworks, and interventions to ensure no Nigerian is left behind.
The Office has successfully presented three Voluntary National Reviews (VNRs) at the United Nations High-Level Political Forum in 2017, 2020, and 2025, showcasing Nigeria’s progress, challenges, and lessons in implementing the SDGs. Beyond policy frameworks, the Office has delivered life-changing projects nationwide, directly impacting communities and accelerating progress towards multiple SDGs.

Strategic Role of OSSAP-SDGs
OSSAP-SDGs has established itself as the coordinating hub for the SDGs in Nigeria. It has:
Mainstreamed the SDGs into national and sub-national development plans.
Strengthened institutional frameworks for planning, data generation, and monitoring.
Mobilised resources and partnerships across government, private sector, and development partners.
Driven impactful intervention projects that touch health, education, infrastructure, women empowerment, ICT, and social protection.
These interventions are not isolated but are strategically aligned with the 17 SDGs, with a focus on poverty reduction, inclusive growth, and human capital development.
Laudable Intervention Projects and Their Impacts
1. Health Sector Interventions (SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being)
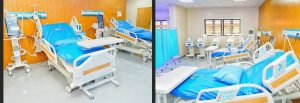
Constructed and fully equipped 40 units of 100-bed Renewed Hope Mother and Child Specialist Hospitals (MCCs) and 30 units of 80-bed MCCs to provide maternal, neonatal, and paediatric care, thereby reducing maternal and child mortality. The Office has commissioned and handed over several of these hospitals for public use, while others are at various stages of completion and handover. To date, hospitals in the following states have been commissioned and handed over: Lagos, Rivers, Anambra, Osun, Oyo, Kwara, Edo, Bayelsa, Akwa Ibom, Imo, Kebbi, Kaduna, Kano, Yobe, Benue, Abia, Ogun, and Ondo, with others scheduled for commissioning in due course.
Constructed and equipped 34 units of 40-bed Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs), 144 units of 20-bed PHCs, and 10 advanced 30-bed PHCs to strengthen Nigeria’s primary health care system, especially in rural areas.
Constructed and equipped specialised facilities like the 200-bed hospital at LASUTH, Paediatric Centre at Federal Medical Centre (FMC) Ebute Meta, and the Sickle Cell Care Centre at Lagos State University Teaching Hospital (LASUTH) to address critical gaps in tertiary healthcare.

Impact: Expanded access to quality healthcare, reduction in preventable deaths, and enhanced health equity across states.
2. Education and Skills Development (SDG 4: Quality Education; SDG 8: Decent Work)
Construction of 11,843 classroom blocks (with additional 383 blocks rehabilitated) furnished with desks and furniture ensures better learning environments. These are spread across all 360 Federal Constituencies of Nigeria.
Supply of 3,406,830 exercise books and 5,943 computers to boost teaching and learning resources.
Establishment of 70 Skill Acquisition Centres to equip youths and women with vocational and life skills for self-reliance.
Construction and furnishing of specialised facilities such as School for the Blind (equipped with Braille machines), the Nana Berry Orphanage Home, and a Girls’ Hostel at National Orthopaedic Hospital, Igbobi to ensure inclusive education.
Impact: Improved enrolment, literacy, inclusivity, and employability of Nigerian youths.
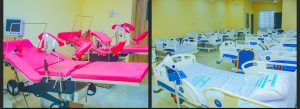
3. Gender Equality and Social Protection (SDG 5: Gender Equality; SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities)
Construction and equipping of 257 bed capacity Transit Homes for Women and Girls each in 3 states to provide safe spaces for vulnerable women and survivors of violence.
Skill Acquisition Centres empower women to become self-sufficient.
In addition, the Office has been empowering 500 women in each state of the Federation and the FCT with skills and resources to promote self-reliance and economic independence.
Targeted projects like orphanages and hostels directly support disadvantaged groups.
Impact: Safer communities, protection of vulnerable women and children, and economic empowerment.
4. Infrastructure and Sustainable Communities (SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure; SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities)
Installation of 71,450 Solar Street Lights enhances safety, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and promotes climate action.
Construction and furnishing of 300 IDP houses and 540 market shops supports displaced persons and boosts small businesses.
Construction of 30 Sports/Youth Centres and Pavilions to provide avenues for youth development, recreation, and talent discovery.
Impact: Improved quality of life, strengthened resilience of communities, and sustainable urban-rural development.
5. ICT and Innovation (SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure; SDG 4: Education)
Construction of 13 ICT/Computer Centres enhances digital literacy.
Provision of computers and e-learning resources to prepare young Nigerians for the digital economy.
Impact: Bridging the digital divide and fostering 21st-century skills.
Rationale Behind the Projects
The interventions are guided by three core principles:
Leaving No One Behind: Prioritising the poor, vulnerable, and marginalised.
Integrated Development: Aligning projects with multiple SDGs simultaneously (health, education, gender, and infrastructure).
Sustainability: Building resilient communities through renewable energy, digital inclusion, and community-based healthcare.

Overall Impact
Through these strategic interventions, OSSAP-SDGs has contributed in:
Expanding access to quality health and education.
Reducing inequalities by empowering women, youths, and vulnerable populations.
Boosting local economies through skills development and market infrastructure.
Strengthening Nigeria’s global image as a committed implementer of the SDGs.
Conclusion
The journey to 2030 is still ongoing, but Nigeria’s strides under OSSAP-SDGs reflect a clear vision and tangible results. By combining policy frameworks, strategic partnerships, and impactful community projects, the Office has transformed the SDGs from abstract global aspirations into real-life benefits for millions of Nigerians.
The achievements so far provide a strong foundation to accelerate progress in the Decade of Action, ensuring that Nigeria not only meets its SDG commitments but also builds a more inclusive, prosperous, and sustainable future.
N/B
This will be back by selected pictures of the projects




