Artificial intelligence (AI) is the emulation of human intelligence through software-coded heuristics. It has become prevalent in various applications, ranging from enterprise software to consumer apps and embedded firmware.
In recent years, AI gained mainstream recognition, with Generative Pre-Training Transformer (GPT) applications like OpenAI’s ChatGPT capturing public fascination. However, AI encompasses much more than just ChatGPT and has diverse applications today.
The key characteristic of AI is its ability to rationalize and take actions that optimize specific goals. Machine learning (ML), a subset of AI, allows computer programs to automatically learn and adapt to new data without human assistance. Deep learning techniques enable automatic learning by processing large amounts of unstructured data, such as text, images, and video.
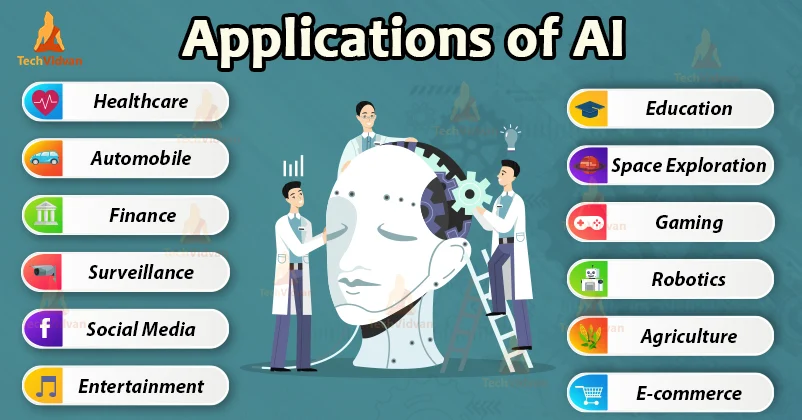
AI Applications
AI finds application across various sectors and industries. In healthcare, AI is used for suggesting drug dosages, treatment identification, and assisting in surgical procedures. Other examples include chess-playing computers and self-driving cars. These AI systems analyze data to make informed decisions and consider the consequences of their actions.
Financial institutions employ AI to detect and flag fraudulent activities, streamline trading, and estimate supply, demand, and pricing of securities.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized into weak and strong AI. Weak AI refers to systems designed to perform specific tasks, like chess-playing programs or voice assistants such as Alexa and Siri.
On the other hand, strong AI exhibits human-like capabilities and handles complex tasks independently, without human intervention. Examples include self-driving cars and AI systems in hospital operating rooms.
Considerations and Controversies
AI has faced scrutiny from scientists and the public, with concerns about its potential risks and ethical implications. There are debates surrounding the idea of machines outpacing human capabilities and redesigning themselves exponentially.
Privacy breaches and the weaponization of AI are also raised as concerns. Additionally, ethical questions arise regarding the treatment of intelligent systems and whether they should possess similar rights to humans.
The impact of AI on employment is another contentious issue. Automation in industries could potentially replace human workers, rendering certain skills obsolete. Self-driving cars, for instance, may reduce the need for traditional taxis and car-sharing services.
While AI offers numerous benefits and advancements, it is important to navigate its development responsibly, considering the potential risks and societal implications.